What is Grassland?
Grassland is an area
where the vegetation is dominated by grasses and other herbs and shrubs.
Examples of grasslands-
1. Steppes- found in Europe and Asia
2. Pampas-
found in South America
3. prairies- found in North America
3. Veldt- found in South Africa an
4. Downs-
found in Australia.
In India, they are
found mainly high Himalayas. The rest of India’s grasslands are mainly composed
of the Steppes and Savana.
What is Grassland
Ecosystem?
The Grassland Ecosystem covers about 10 percent of the Earth's
surface. It is found where rainfall is about 15-75 cm per year not enough to
support a forest, but more than that of true desert. Grassland ecosystem is an interaction
between living organisms with each other and nonliving components of the grassland
area.
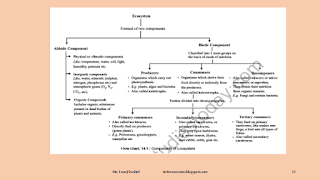
Components of
Grassland Ecosystem
The
chief components of the Grassland Ecosystem are as below:
1.
Abiotic
Components:
These are non-living thing
components consist of light, temperature, soil, rainfall, organic
substances and inorganic substances such as carbon, hydrogen, sulphur, nitrogen
and phosphorous etc.
2. Biotic Components:
These are living components and they are grouped into following three groups.
(I) Producers:
In grassland, the
primary producers of food are the grasses such as Aristida,
Cynodon, Digitaria, Desmodium, Setaria etc and herbs and
shrubs.
(II) Consumers:
The consumers are
heterotrophic organisms in a grassland ecosystem. They are of three types.
(a)
Primary
consumers (Herbivores):
These feed directly
from the grasses and include herbivores / grazing animals such as Cows, Buffaloes, bisons Goats, Rabbits, Mouse, Deers, etc. and also insects like grasshopper, leafhoppers
etc, termites, centipede, millipedes etc.
(b) Secondary consumers
(First carnivores):
These consumers are
the carnivorous animals such as snakes, lizard, jackal,
foxes, frogs, burrowing Owl, prairie dogs
etc. which feed on the primary consumers.
(c) Tertiary
consumers (Second carnivores):
The tertiary
consumer in the grassland ecosystem includes Hawk, Eagles and
vultures which prey upon the secondary and primary consumer.
(III)
Decomposers: